Yesterday I reported that Qualcomm might launch the Qualcomm Snapdragon 775G, I was sceptical as this is normally launched during the Tech Summit in December.
Well, it turns out they have launched a new chipset, and it looks very impressive, likely to compete with other low-cost 5G options from MediaTek and Hisilicon/Huawei.
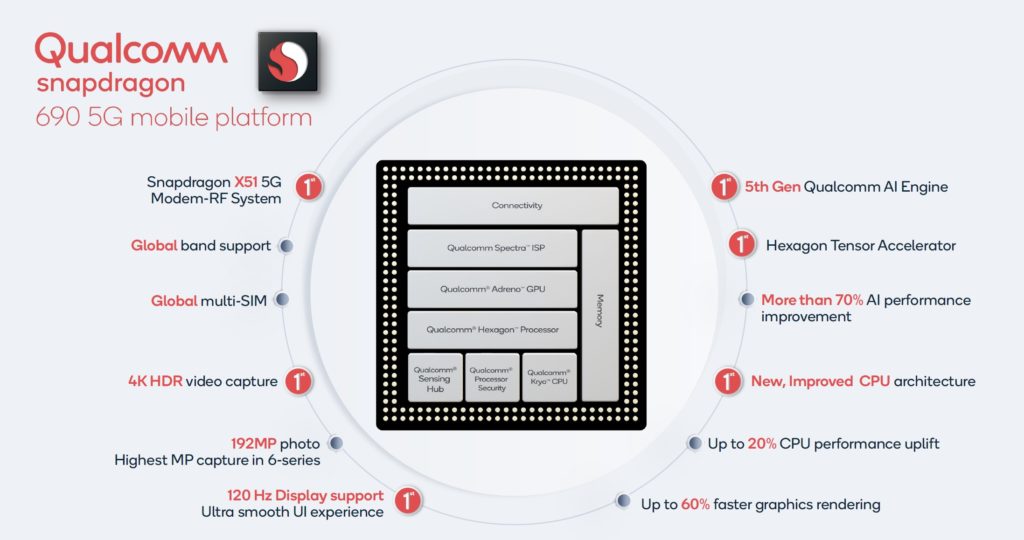
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 600-series now has a 5G chipset, and on paper, it looks better than the Snapdragon 765 is some regards.
CPU & Fabrication Process

The new chipset is fabricated on the 8nm LPP fabrication process, which is a big drop from the 11nm LLP used on the SD765 which was launched two years ago or the SD670 which used the 10 nm LPP process.
This is the same fabrication process as the Qualcomm Snapdragon 720G while being a little smaller than the 7nm EUV for the SD765G.
Qualcomm keeps the standard 2×6 CPU configurations in terms of big and little core but what is interesting is the use of two Kryo 560 cores which are based on the Arm Cortex-A77 IP. This then, therefore, gives the chipset an advantage over the A76 based Snapdragon 765G.
However, it is worth noting that the SD765G has one core clocked at 2.4GHz and the second at 2.2GHz whereas the SD690 has both its big cores clocked at 2.0GHz.
Then the Snapdragon 690 has its six Kryo 560 (Cortex A55) cores clocked at 1.7GHz vs 1.8Ghz of the SD765G.
So, it is unlikely the SD690 will outperform the SD765G across all cores, but it will be interesting to see how closely they are batch on single-core CPU tests.
With the Snapdragon 720G you get
- 2x Cortex-A76 @ 2.3GHz
- 6x Cortex-A55 @ 1.8GHz
And the older SD730G had the same spec, but the A76 was clocked .1Ghz lower at 2.2GHz
Dropping down to the SD675 you get:
- 2x Kryo 460 (CA76) @ 2.0GHz
- 6x Kryo 460 (CA55)@ 1.7GHz
The Snapdragon 670 has:
- 2x Kryo 360 (CA75) @ 2.0GHz
- 6x Kryo 360 (CA55) @ 1.7GHz
GPU

With Qualcomm GPUs, it is harder to compare the exact spec, as they only provide the name of the GPU and no details.
The Snapdragon 690 uses a new Adreno 619L design and Qualcomm claim up to 60% increase in performance compared to the previous generation Snapdragon 675 which had an Adreno 612. Which is an impressive jump in performance, going from the SD730G to the SD765G, Qualcomm claimed a 38% performance gain. I found the GPU on the TCL 10 Pro, which uses the SD675 to be quite poor, so it is perhaps no surprise to see such a big jump in performance.
If you look at the Snapdragon 670, which is lower down the ladder, that actually has an Adreno 615 which benchmarks higher in most GPU tests. So that 60% gain over the SD765 drops down quite a bit when you compare it to a lower down chipset.
For the Snapdragon 720G this has a Adreno 618 and this was reported as running at 500 MHz, whereas the SD730G was running at 575 MHz. This would, therefore, give the impression that the SD690 could have a more powerful GPU, but that remains to be seen.
Finally, it is almost certain that the Snapdragon 765G will outclass the SD690 with its Adreno 620 GPU running @ 625MHz.
Memory
As for the memory, all the 600-series options in this comparison use LPDDR4X running at 1866MHz with dual 16-bit channel support.
This is also the same for the SD720G and the 730G.
The Snapdragon 765G runs faster with 2133MHz giving 17.0GB/s vs 14.9GB/s from the others.
Connectivity

The big one here is that the Snapdragon 690 is a 5G chipset, it uses an integrated Snapdragon X51 which is a step down from the X52 found on the Snapdragon 765G.
The modem now adds support for 5G sub-6GHz with global band support. The speeds here scale up to 2500Mbps downstream and 1200Mbps upstream on sub-6 networks, utilising up to 100MHz of spectrum bandwidth. There is no mmWave connectivity which is not a big issue for most markets.
For the SD765G that has 5G NR Sub-6 4×4 100MHz and mmWave 2×2 400MHz this then allows it to hit download speeds of 3700 Mbps and upload speeds of 1600 Mbps.
All the other chipsets are 4G/LTE using either the Snapdragon X12 LTE or Snapdragon X15 LTE
Wi-Fi 6
It is also worth noting that this chipset is Wi-Fi 6 ready. So phones launched with it may optionally use it.
- Wi-Fi Standards: 802.11a/b/g/n, 802.11ax-ready, 802.11ac Wave 2
- Qualcomm® Wi-Fi 6-ready technology features: Target Wakeup Time, 8×8 sounding, WPA3 security support
- MIMO Configuration: 2×2 (2-stream)
- Wi-Fi Features: 8×8 Sounding
Apart from the SD765G, all the other chipsets used Wi-Fi 5
Other Features

The Spectra ISP for the camera has also been upgraded bring it in line with the higher end chips. It now offers support up to 192MP still pictures or up to 48MP sensors with multi-frame noise reduction or a dual-camera setup in tandem of 32+16MP sensors. The chip has a 10-bit capture and display pipeline, allowing it 4K HDR capture and display – although we didn’t see mention of 4K60 recording.
The older 600 series chips had a Spectra 250 with support for 25MP single / 16MP dual

Benchmarks – Antutu, 3D Mark and Geekbench
Currently, there are no benchmarks, it has only just been announced, however, as Qualcomm announced a 60% performance boost from the SD670 I will list some stats for reference and add the benchmarks as they come in.
- Snapdragon 765G
- Antutu V8 – 298925 Points (total) 93039 (GPU) 86677 (CPU)
- Geekbench 5.1 – 595 Single, 1676 multi
- Snapdragon 720G (Realme 6 Pro)
- Antutu V8 – 282336 Points (total) 71575 (GPU) 101864 (CPU)
- Geekbench 5.1 – 568 Single, 1643 multi
- Snapdragon 675 (TCL 10 Pro)
- Antutu V8 – 219353 Points (total) 36059 (GPU) 88028 (CPU)
- Geekbench 5.1 – 595 Single, 1676 multi
- Snapdragon 670
- Antutu V8 – 190072 Points (total) 49010 (GPU) 67715 (CPU)
- Geekbench 5.1 – 595 Single, 1676 multi
Qualcomm Snapdragon 690 vs SD 675 vs SD720 vs SD 765G Specification Comparison Table
| SoC | Snapdragon 690 | Snapdragon 765G | Snapdragon 730G | Snapdragon 720G | Snapdragon 675 | Snapdragon 670 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | 2x Kryo 560 (CA77) @ 2.0GHz |
1x Cortex A76 @ 2.4GHz (765G) | 2x Cortex-A76 @ 2.2GHz | 2x Cortex-A76 @ 2.3GHz | 2x Kryo 460 (CA76) @ 2.0GHz |
2x Cortex-A76 @ 2.3GHz |
| 1x Cortex-A76 @ 2.2GHz | ||||||
| 6x Kryo 560 (CA55) @ 1.7GHz |
6x Cortex-A55 @ 1.8GHz | 6x Cortex-A55 @ 1.8GHz | 6x Cortex-A55 @ 1.8GHz | 6x Kryo 460 (CA55) @ 1.7GHz |
6x Cortex-A55 @ 1.8GHz | |
| GPU | Adreno 619L | Adreno 620 @ 625MHz | Adreno 618 @ 575 MHz | Adreno 618 @ 500 MHz | Adreno 612 | Adreno 618 @ 500 MHz |
| 60% perferformacne vs 675 | +38% perf vs 730G | |||||
| DSP / NPU | Hexagon 692 |
Hexagon 696 | Hexagon 688 | Hexagon 688 | Hexagon 685 | Hexagon 688 |
| HVX + Tensor | HVX + Tensor 5.4TOPS AI | HVX + Tensor | HVX + Tensor | HVX + Tensor | HVX + Tensor | |
| Memory Controller | 2x 16-bit CH | 2x 16-bit CH | 2x 16-bit CH | 2x 16-bit CH | 2x 16-bit CH | 2x 16-bit CH |
| @ 1866MHz LPDDR4X 14.9GB/s | @ 2133MHz LPDDR4X / 17.0GB/s | @ 1866MHz LPDDR4X 14.9GB/s | @ 1866MHz LPDDR4X 14.9GB/s | @ 1866MHz LPDDR4X 14.9GB/s | @ 1866MHz LPDDR4X 14.9GB/s | |
| ISP/Camera | Spectra 355L | Dual 14-bit Spectra 355 ISP | Dual Spectra 350 ISP | Dual Spectra 350 ISP | Spectra 250 | Dual Spectra 350 ISP |
| 48MP single 32+16MP dual | 1x 192MP or 36MP with ZSL 2x 22MP with ZSL |
1x 36MP with ZSL 2x 22MP with ZSL |
1x 36MP with ZSL 2x 22MP with ZSL |
25MP single / 16MP dual | 1x 36MP with ZSL | |
| Integrated Modem | Snapdragon X51 | Snapdragon X52 Integrated | Snapdragon X15 LTE | Snapdragon X15 LTE | Snapdragon X12 LTE | Snapdragon X12 LTE |
| (LTE Category 24/22) | (LTE Category 24/22) | (Category 15/13) | (Category 15/13) | (Category 12/13) | (Category 12/13) | |
| DL = 1200 Mbps | DL = 1200 Mbps | DL = 800Mbps | DL = 800Mbps | DL =600Mbps | DL = 600Mbps | |
| UL = 210 Mbps | UL = 210 Mbps | UL = 150Mbps | UL = 150Mbps | UL = 150Mbps | UL = 150Mbps | |
| 5G NR Sub-6 | 5G NR Sub-6 4×4 100MHz + mmWave 2×2 400MHz | |||||
| DL = 2500 Mbps | DL = 3700 Mbps | |||||
| UL = 1200 Mbps | UL = 1600 Mbps | |||||
| Fabrication Process | Samsung | Samsung | Samsung | Samsung | Samsung | Samsung |
| 8nm LPP | 7nm EUV (7LPP) | 8nm (8LPP) | 8nm (8LPP) | 8nm (8LPP) | 8nm (8LPP) |