Qualcomm has thrown a curveball with the naming of their new flagship chipset. What was expected to be the Snapdragon 875 has now become the Snapdragon 888.
The naming convention is due to 888 being regarded by the Chinese as a symbol of fortune and prosperity, though I am not sure why they opted to use it this year rather than next when the 885 would have been due. One possible explanation is an olive branch to those in the industry caught up in the ongoing China-US trade war.
Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 vs Snapdragon 865 vs Kirin 9000 Specification Comparison
| SoC | Snapdragon 888 | Snapdragon 865 | Kirin 9000 5G | Exynos 2100 (Rumoured) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | 1x ARM Cortex-X1 @ 2.84 GHz | 1x Cortex-A77@ 2.84GHz | 1x Cortex A77 @ 3.13Ghz |
1x ARM Cortex-X1 @ 2.91Ghz |
| 3x ARM Cortex-A78 @ 2.42 GHz | 3x Cortex-A77@ 2.42GHz | 3x Cortex A77 @ 2.54Ghz |
3x ARM Cortex-A78 @ 2.81Ghz | |
| 4x ARM Cortex-A55 @ 1.8 GHz | 4x Cortex-A55 @ 1.80GHz | 4x Cortex A55@ 2.05Ghz |
4x ARM Cortex-A55 @ 2.21Ghz | |
| GPU | Qualcomm Adreno 660 +35% perf |
Adreno 650 @ 587 MHz | Mali-G78 24 Cores |
Mali-G78 MP |
| APU / NPU / AI Proc. / Neural IP | Hexagon 780 26 TOPS AI |
Hexagon 698 15 TOPS AI |
2 big core, 1 tiny core | ? |
| Memory | 3200MHz LPDDR5 / 51.2GB/s 3MB system level cache |
2133MHz LPDDR4X / 33.4GB/s or 2750MHz LPDDR5 / 44.0GB/s 3MB system level cache |
LPDDR5 / LPDDR 4X | ? |
| ISP/Camera | Triple 14-bit Spectra 580 ISP 1x 200MP or 84MP with ZSL 64+25MP with ZSL 3x 28MP with ZSL 4K video & 64MP burst capture |
Dual 14-bit Spectra 480 ISP 1x 200MP or 64MP with ZSL 2x 25MP with ZSL |
quad-core, 6th gen ISP
|
? |
| Modem | X60 integrated (5G NR Sub-6 + mmWave) DL = 7500 Mbps UL = 3000 Mbps |
X55 external 5G NR Sub-6 + mmWave) DL = 7000 Mbps UL = 3000 Mbps |
Balong 5000 4G + 5G NR NSA+SA Sub-6GHz |
|
| Process | Samsung 5nm (5LPE) |
TSMC 7nm (N7P) |
TSMC 5nm |
Samsung 5nm (5LPE) |
Manufacturing Process
Like most flagship chipsets in the upcoming year, the Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 will be fabricated on the 5nm fabrication process; this is the same as the Huawei/HiSilicon Kirin 9000,
The Snapdragon 865 and the Plus model were both using the 7nm fabrication process.
However, it is worth noting that Qualcomm has switched to the Samsung 5nm fabrication process. This could play out to be interesting because the upcoming flagship Samsung chipset will share the same fabrication process, and likely same CPU design. The biggest difference will be the GPU. So, after years of the Exynos being inferior to Snapdragon, it could end up even this year.
For the fabrication process itself, Samsung claims a 20% decrease in power consumption at the same performance, or a 10% increase in performance at the same power, together with a 20% area reduction.
CPU
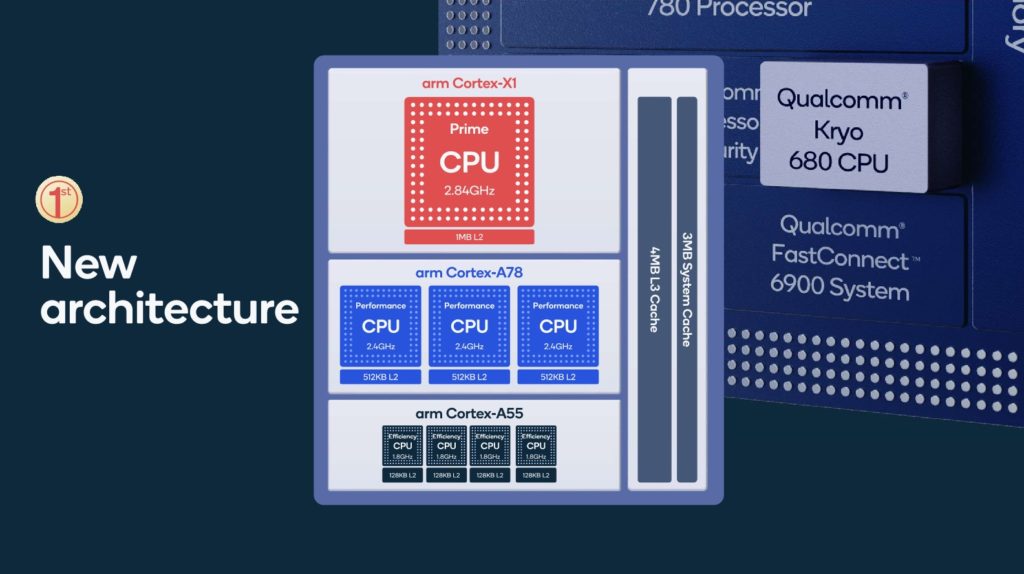
Here’s where things get a little more interest. Qualcomm is the first company to officially launch a chipset with the Arm Cortex-X1. This will be a single core which is then combined with three Arm Cortex-A78 cores.
Currently, it is only the Samsung Exynos 1080 that uses Arm Cortex-A78 cores, but this is an upper mid-range chipset, and the flagship model is also expected to use the Cortex-X1.
The X1 focuses on maximising performance at the cost of lesser power efficiency, which is why we only see one of these used. Arm claimed +30% increase in IPC over the last generation Cortex-A77, while Qualcomm has stated a 25% uplift.
Interestingly, the frequencies are identical to the original Snapdragon 865. So the increase in performs appears to be entirely down to the improved CPU architecture.
HiSilicon opted to use the older Arm Cortex A77 cores, but at a higher frequency.
Early rumours have the Exynos at higher frequencies, but this remains to be seen.
GPU

As always with Qualcomm, they do their own GPU, in this case, it shifts from the Adreno 650 to Adreno 660.
The new Adreno GPU targets 144fps gaming and supports updateable GPU drivers. This is the “most significant upgrade in Qualcomm Adreno GPU performance,” according to the company.
I am sure each year is the most significant upgrade in Qualcomm Adreno GPU performance, however, they promise a 35% increase in performance vs last year combined with 20% more power efficiency.
This is one area where HiSilicon will be tough to beat, the Kirin 9000 uses the latest Arm Mali G78 GPU and has a massive 24 cores.
Memory
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 865 was compatible with both LPDDR4X and LPDDR5, though most phones used LPDDR5.
This year Qualcomm only list LPDDR5, and the frequencies are increased too, going from 2750MHz to 3200MHz which results in 16.4% more bandwidth than the last generation with 51.2GB/s.
Camera and Image Processing
In recent years we have seen manufactures vastly improve their cameras, and this has quickly become the difference between premium flagship devices and affordable.
With a growing number of cameras on phones, this has led to Qualcomm adding a third ISP to the SoC, allowing the SoC to now run three independent camera modules concurrently.
The new triple-ISP architecture now increases the overall pixel processing throughput by 35% to 2.7 Gigapixels/s. This would allow three 28MP sensors with zero shutter lag to be used concurrently, or alternatively 64+25MP sensors with ZSL or a single 84MP sensor with ZSL.
No AV1 Decoding
Bizarrely, Qualcomm continues to shun AV1 decoding; this means it is just MediaTek that offer this functionality. AV1 is still limited, but Netflix did start to offer it this year.
Artificial Intelligence
Each company has a different approach to AI, Qualcomm has their Hexagon DSP, which is now the Hexagon 780.
This is another area where Qualcomm is stating massive gains vs the previous generation. There is 16 times more dedicated memory with a 3 fold increase in performance per watt, this results in a 50% improvement in scalar execution capabilities and twice the tensor execution throughput.
Wi-Fi 6E Supported & Bluetooth 5.2
As I predicted in my Wi-Fi 6E posts, the Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 will be the first device to support the improved Wi-Fi 6E standard. The only difference between this and the existing Wi-Fi 6E is that it can use the new 6Ghz channel, which is far less congested and has many more channel options.
Currently, there are no routers on the market with Wi-Fi 6E. Furthermore, when there are, it is likely to be very expensive. It is possible we will only see tri-band systems at first because a dual-band system would only be able to support 5GHz or 6Ghz.
The chipset will also support Bluetooth 5.2, which offers a few advantages over the older version.
5G Connectivity
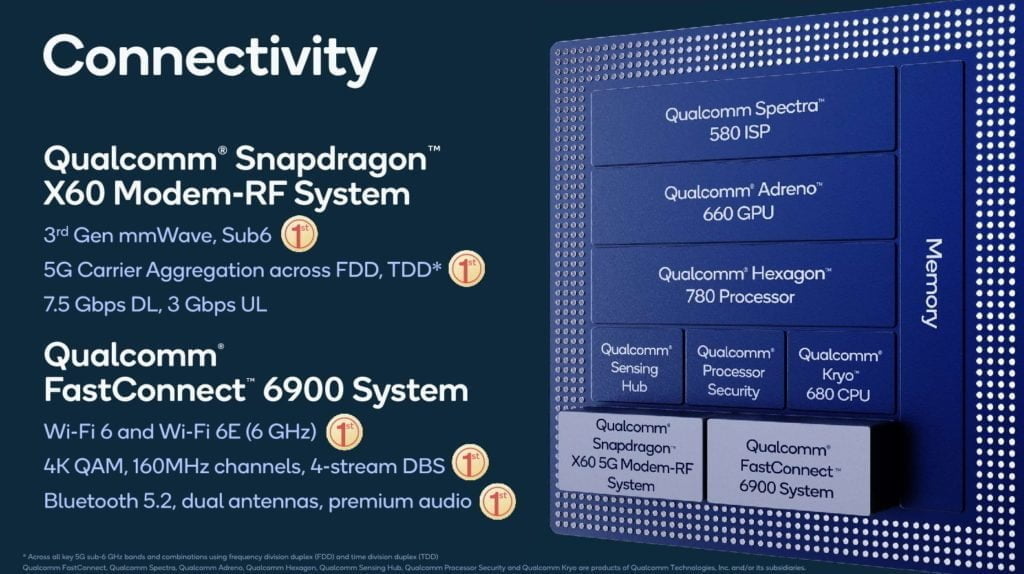
Since 5G launched on Qualcomm devices, they have had to use an external modem, but Qualcomm has finally integrated this onto the main SoC with the new X60 modem.
Benchmarks
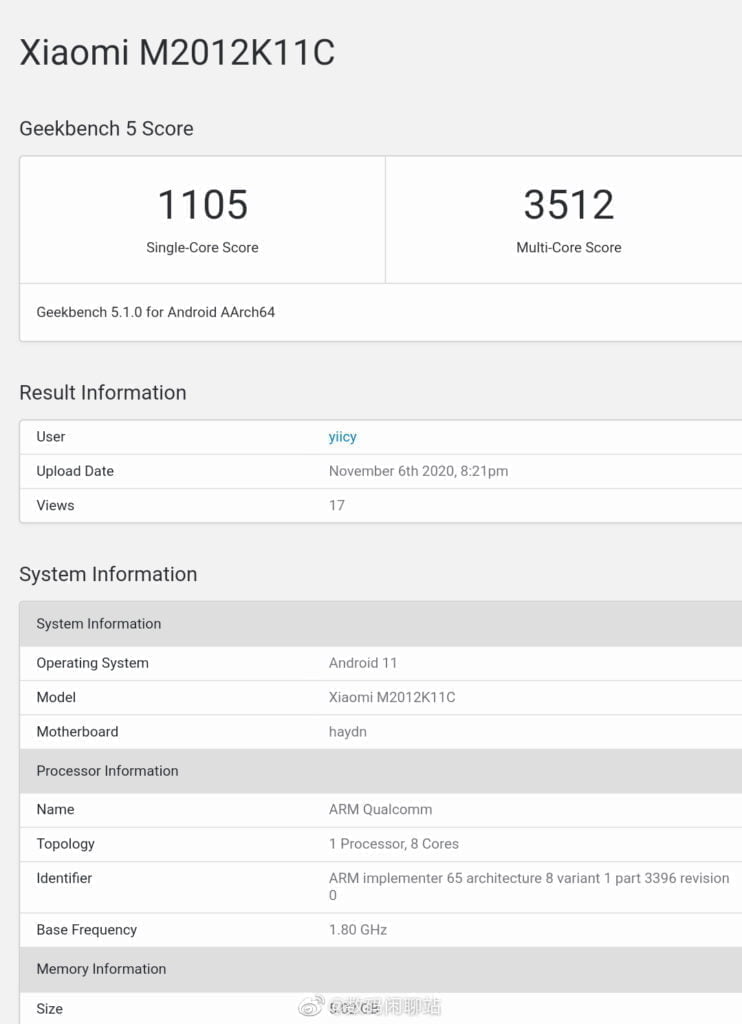
No official benchmarks, but early leaks have come out. I’d take them with a pinch of salt.
The most authentic is the Geekbench leak of the Xiaomi Mi 11.
With the Kirin 9000 5G already on the market, there are plenty of benchmarks for this. It currently sits at the top of the Antutu benchmarks and is easily the most powerful chipset on the market (temporarily).
| Single-core | Multi-core | |
| Snapdragon 875 | 1,204 | 4,121 |
| Snapdragon 875 Leak 2 | 1,105 | 3,512 |
| Exynos 2100 | 1,323 | 4,215 |
| Kirin 9000 5G | 920 / 1020 | 3275 / 3704 |
| Antutu | |
| Snapdragon 875 | 847,868 |
| Exynos 2100 | ? |
| Kirin 9000 5G | 531270 / 686835 |
Phones with the Qualcomm Snapdragon 888
The chipset has only just been announced, so no phones yet, however, most companies have already backed the chipset, as you would expect.
Xiaomi is claiming the Mi 11 will be the first to launch, I am sure they said this last year, and Samsung was the first out the door as usual.
Realme have teased their phone codenamed Race; then OPPO has also confirmed the next Find X device will have it.
Even Motorola plan to launch a new phone using the Snapdragon 888
Posted by Mighty Gadget Blog: UK Technology News and Reviews